Table Of Content
A lack of fidelity and functionality is a significant problem for interaction designers when prototyping and testing using traditional image-based design tools. Interaction design is a process of making human-to-computer interfaces (HCI) feel human-like. Interactive digital products create this “human” connection by giving feedback to the end-users. The feedback can be through a scroll-provoked animation, clicked state of a button or transition to another page.
How to Create Intuitive Products by Imitating Physicality
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience. In the third and the fourth lessons, you’ll learn about the most common UX design tools and methods. You’ll also practice each of the methods through tailor-made exercises that walk you through the different stages of the design process. There are many valuable tools and resources out there to help you learn interaction design. With a combination of self-study and professional instruction, you can build a well-rounded skill set and take the first step towards a career in the field. If you’re reading this guide with your own career in mind, you may be curious about the kinds of jobs that are available within the field of interaction design—and how much they pay.
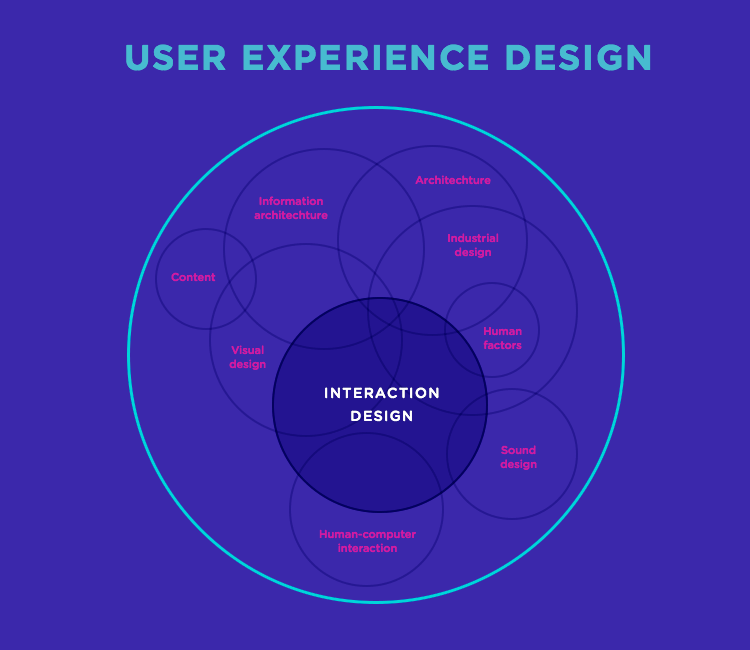
What is Interaction Design?
It creates a bounce that serves as an anticipatory action, preparing the users for the main action. For example, think about adding some sound or haptics to animations when a user completes a particular task. Another best use of time is the progress bar animation, where you can see and track the progress of a particular task or process. Visual representation is all about the graphical elements like images, typography, and icons that users interact with.
Interactions
They are responsible for making sure that the human experience with technology is as intuitive as possible. The golden rule of interaction design is to design the interface and user experience so that it’s intuitive and easy to use. Effective use of visual elements can establish a hierarchy of information, guide users through the interface, and create a positive emotional response. A well-designed visual representation can lead to increased user engagement, improved brand perception, and greater success for the product or service.
Affinity Diagrams: How to Cluster Your Ideas and Reveal Insights
Whatever animations, states, and other interactivity developers program and save to the repository are available to designers in UXPin. Mobile interactions are typically called gestures because users interact with a device using hand and finger motions. Few fields prove more rewarding for those energised by fusing analytics, emotions, and engineering to forge helpful products. Anybody can start learning the fundamentals and experimenting with ideas today right away. Masterful execution weaves dozens of minute interface details into effortless, empowering user journeys.
Book Review: Thoughts on Interaction Design, by Jon Kolko - Core77.com
Book Review: Thoughts on Interaction Design, by Jon Kolko.
Posted: Mon, 30 Apr 2007 07:00:00 GMT [source]
The interactive design degree equips you with core methods and tools to lead design teams and impact user experiences throughout your career. Every technology interaction you experience in a day—from using mobile apps to playing games to wearing smart accessories to engaging with other digital environments—has been designed to maximize user experience (UX). User experience designers apply UX fundamentals like design thinking, human-centered design, and user research to make decisions. They’re specifically concerned with a user’s tasks, actions, and environment, while interaction designers focus on making the digital product respond to user actions in an appropriate way. They tend to think about what happens when a user clicks a button, types a phrase into a search bar or hovers over an image. With the knowledge and principles outlined in this guide, you are well-equipped to begin your journey into the fascinating world of interaction design.
The animation starts fast, then slows, and goes past the ending keyframe’s value. It is opposite the Ease In curve, where the animation starts fast and slows down towards the end. It works well for moving objects into view and reinforcing crucial visual information. This preset creates an animation that starts slowly and accelerates as it reaches the end. Whereas delay refers to how long it takes after the trigger for the animation to begin.
This specialization is especially known for project-based design courses where students work on teams to create prototypes of products that provide tangible benefits to specific user groups. Students can package those project experiences together into an online portfolio to make themselves more competitive when applying to technology industry jobs and graduate schools. It’s a whole discipline in and of itself, and it adds interactivity to the two-dimensional visual design of user interfaces to augment user experiences.
In the upcoming sections, we will delve deeper into real-world examples and case studies that offer a more tangible understanding of the work of Interaction Designers. It’s easy to admire the effect as a whole without looking past it at the nuts and bolts—the elements that are set together so well and according to age-old principles so as to create that ‘wow’ effect. Scale can be used to create a hierarchy for and add emphasis to certain elements on a design.
If you’re interested to find out more about interaction design, you can read Interaction Design – brief intro by Jonas Lowgren, which is part of our Encyclopedia of Human-Computer Interaction. It provides an authoritative introduction to the field, as well as other references where you can learn more. As you can see, interaction design skills open the door to a variety of exciting career paths.

It weaves the complex tapestry of user interaction with the digital platform, ensuring seamless, intuitive, and responsive experiences. For instance, consistency ensures that controls remain uniform throughout a design, while proximity suggests related items be grouped. Visual hierarchy places importance on presenting the most vital information at the top. By understanding and applying these principles, designers can create intuitive, aesthetically pleasing, and practical designs that cater to user needs and preferences. Balance can be achieved symmetrically, where elements mirror each other on either side of a central axis, or asymmetrically, where elements provide equilibrium without mirroring. It ensures that viewers can engage with the content without feeling overwhelmed or distracted.
A great way to break into the field is by specializing in an area interaction design. Good IxD ensures that users can easily and efficiently accomplish their goals, whether they are using a website, mobile app, or physical product. This can improve user satisfaction and loyalty, as well as increase conversions and sales. The Interaction Design Foundation describes user experience design in terms of the What, Why, and How of product use.
Interaction designers utilize all five dimensions to consider the interactions between a user and a product or service in a holistic way. Specifically, we use them to help envision the real-world demands of a usership in relation to a design not yet introduced. An interaction designer focuses on user data, research, etc. when a user interacts with the product. Their goal is to generate concepts that enable seamless and relevant experiences when users make a move.
Careers progressing from early execution roles up through strategic leadership see designers evolving into experienced directors. They help set long-term product visions, balancing business objectives with user needs analysis. Ultimately, proficiency results from substantial practice across the lifecycle – researching, ideating, designing, testing, and refining designs guided by user truths rather than assumptions. Specific recurring modules form the backbone of nearly all digital interfaces, from webpages to mobile apps. While specifics and priorities differ across contexts, mastery over crafting and connecting these core components is fundamental.
For a deeper dive into the intricacies of visual composition, including balance, refer to the article on the building blocks of visual design at interaction-design.org. Designers use principles such as visibility, findability and learnability to address basic human behaviors. Design principles are guidelines, biases and design considerations that designers apply with discretion. Professionals from many disciplines—e.g., behavioral science, sociology, physics and ergonomics—provided the foundation for design principles via their accumulated knowledge and experience. Interactive prototypes are working models designers create to allow target users to interact with a test of your application.
Not only can you make an element stand out this way—you can also use scale to create a sense of depth (since nearer objects appear larger to the human eye). Exaggerated scales of images also add a certain level of interest and drama to them. We use colours in visual design to convey emotions in and add variety and interest to our designs, separate distinct areas of a page, and differentiate our work from the competition. Some designs make use of negative space to create interesting visual effects. For example, the famous World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) logo makes use of the confusion between positive shape and negative space to create the image of a panda. Lines are strokes connecting two points, and the most basic element of visual design.
No comments:
Post a Comment